In the vast expanse of global economics, few metrics hold as much sway and significance as Eurozone inflation data. It stands as a beacon, illuminating the path of economic health and stability for the interconnected web of nations within the Eurozone. For regions like Dubai, with intricate ties to the Eurozone, understanding the intricacies and implications of this data is not merely advisable but essential for informed decision-making and strategic planning.
The Significance of Eurozone Inflation
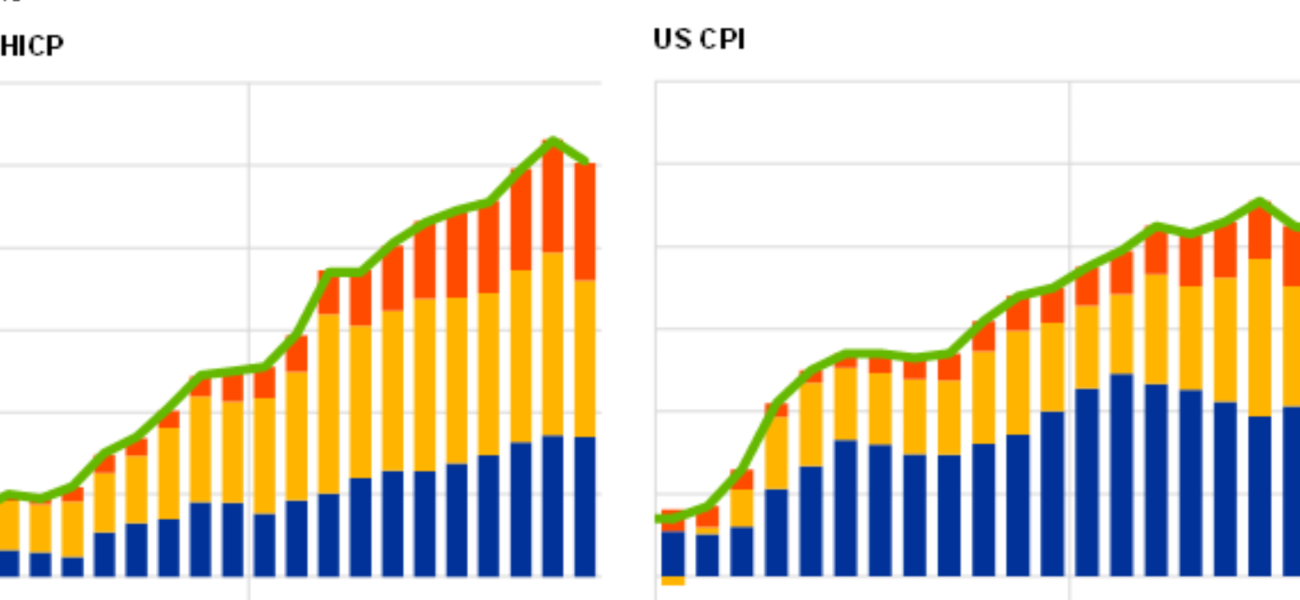
Eurozone inflation data is not just a set of numbers; it’s a reflection of the pulse of an entire economic bloc. At its core, it encapsulates the rate at which prices of goods and services are ascending within the member countries of the Eurozone. This metric serves as a fundamental barometer for assessing the overall economic climate, influencing a myriad of factors ranging from central bank policies to interest rates and investor sentiments.
Key Metrics in Eurozone Inflation
Central to the realm of Eurozone inflation data lie several key metrics that offer insights into the economic landscape.
Consumer Price Index (CPI):
The CPI serves as a litmus test for inflation, measuring the average change over time in the prices paid by urban consumers for a basket of consumer goods and services. Its fluctuations reverberate through economies, signaling periods of inflationary pressure or deflationary trends.
Producer Price Index (PPI):
Complementary to the CPI, the PPI tracks the average changes in prices received by domestic producers for their output. It provides invaluable insights into inflationary pressures at the production level, often serving as a harbinger of future trends in consumer prices.
Core Inflation:
Stripping away the veneer of volatility, core inflation excludes volatile components such as food and energy prices, offering a more stable measure of underlying inflationary trends within the Eurozone economy.
Recent Trends in Eurozone Inflation
Despite concerted efforts by policymakers, the Eurozone has found itself ensnared in the quagmire of persistently low inflation rates in recent years. This phenomenon, commonly dubbed “lowflation,” presents multifaceted challenges to economic growth, wage dynamics, and debt sustainability within the region. The specter of deflation lurks on the horizon, casting a pall over the prospects of robust economic recovery.
Factors Influencing Eurozone Inflation
Delving into the intricacies of Eurozone inflation unveils a tapestry woven with a myriad of factors.
Monetary Policy:
The European Central Bank (ECB) wields considerable influence over inflationary dynamics through its monetary policy decisions. Interest rate adjustments, quantitative easing programs, and forward guidance mechanisms form the cornerstone of its arsenal in combating inflationary or deflationary pressures.
Global Economic Trends:
The Eurozone does not exist in isolation; it is intricately intertwined with the ebbs and flows of the global economy. Geopolitical tensions, trade dynamics, and commodity price fluctuations exert palpable influence on Eurozone inflation, cascading through supply chains and consumer behavior.
Domestic Demand and Supply Dynamics:
At the heart of Eurozone Dubai lies the intricate dance between domestic demand, labor market conditions, and supply chain disruptions. Wage dynamics, consumer spending patterns, and production bottlenecks collectively shape the inflationary landscape, reflecting broader economic trends and sentiments.
Implications for Dubai
For a bustling economic hub like Dubai, the ripples of Eurozone inflation data are not mere ripples but seismic waves with far-reaching implications.
Trade and Investment:
Dubai’s economic fortunes are intricately linked with the Eurozone through robust trade and investment channels. Fluctuations in Eurozone inflation can ripple through these channels, impacting trade volumes, investment flows, and overall economic sentiment.
Currency Dynamics:
The Eurozone’s economic health influences currency dynamics, with repercussions for exchange rates and currency markets. For Dubai, a keen understanding of these dynamics is indispensable for managing currency risks and optimizing international trade.
Strategies for Mitigating Risks
Navigating the choppy waters of Eurozone inflation requires foresight, adaptability, and strategic acumen.
Diversification:
Diversifying trade partnerships and investment portfolios beyond the Eurozone can cushion Dubai’s economy against the impact of Eurozone inflationary fluctuations.
Risk Management:
Implementing robust risk management strategies, including hedging against currency risks and commodity price fluctuations, can fortify Dubai’s resilience in the face of economic uncertainties.
Sectoral Focus:
Focusing on sectors resilient to inflationary pressures, such as technology, healthcare, and renewable energy, can position Dubai’s economy for sustained growth amidst Eurozone uncertainties.
Eurozone inflation data is not merely a statistic; it’s a narrative, weaving together the threads of economic health, policy decisions, and global interconnectedness. For regions like Dubai, understanding the implications of Eurozone inflation is not an option but an imperative. By deciphering the trends, navigating the risks, and seizing the opportunities embedded within Eurozone inflation data, Dubai can chart a course towards prosperity in an ever-evolving global economic landscape